Nigel Wood’s Percentage Method
In Chinese Glazes, Chapter 13, p 249-262, Nigel Wood describes how to use the percentage method to reconstruct glaze analyses using modern materials.
Example Analysis
To illustrate the percentage method, let’s use a typical glaze analysis from Chinese Glazes:
Table 29 Hanghzou Guan wares and Longquan Guan wares compared, Glazes-Hangzhou, Guan 1. Nigel Wood, Chinese Glazes, p. 82
Hangzhou Guan Glaze 1
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
| Adjusted Total (100%) | 65.74 | 14.68 | 0.70 | 13.47 | 4.02 | 0.20 | 4.22 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
View this analysis on Glazy: https://glazy.org/recipes/3825
Determining which materials to use
From the analysis we need materials that have the following oxides: SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO, K2O, Na2O, P2O5, Fe2O3, and TiO2. Looking through the analyses for materials in our studio we find:
- Feldspars: K2O, Na2O, SiO2, and Al2O3. Due to the prevalence of K2O in this analysis, we will use Potash Feldspar.
- Kaolin: SiO2 and Al2O3
- Dolomite: MgO and CaO
- Bone ash: P2O5 and CaO
- Silica: SiO2
- Whiting: CaO
- Red Iron Oxide: Fe2O3
When fulfilling oxides in the analysis, we will do so in order of material complexity. For example, we will use Potash Feldspar to fulfill Na2O and K2O before using Silica to fulfill SiO2. If we used Silica first to add all of the SiO2, adding any Potash Feldspar later would give us too much SiO2.
Note: These materials are theoretical. In practice it is better to use analyses for specific materials, e.g. Custer Feldspar instead of Potash Feldspar and EPK instead of Kaolin.
1. Add Potash Feldspar to fulfill K2O and Na2O (combined values as KNaO):
Here is our analysis for theoretical Potash Feldspar:
| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | KNaO | LOI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potash Feldspar | 64.76% | 18.32% | 16.92% | 16.92% | 100 |
We use Feldspar to fulfill the R2O oxides, K2O and Na2O. The easiest way to do this is to combine K2O and Na2O into a single value, KNaO. To calculate the amount of Potash Feldspar we need, divide the KNaO value (4.2) by Potash Feldspar’s KNaO value (16.92) and then multiply by 100:
4.20 / 16.92 * 100 = 24.8
Now that we know we need 24.8% Potash Feldspar to fulfill KNaO, we can calculate the other oxides in Potash Feldspar:
SiO2: 64.76 * .248 = 16.06
Al2O3: 18.32 * .248 = 4.54
The resulting calculation table looks like this:
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.06 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
2. Add Kaolin to fulfill Al2O3 and some SiO2
Here is our analysis for theoretical Kaolin:
| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | KNaO | LOI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolin | 47.29% | 40.21% | 12.50 | 100 |
We will use Kaolin to fulfill the remaining Al2O3 and some SiO2. To calculate the amount of Kaolin we need, divide the Al2O3 value (10.05) by Kaolins’s Al2O3 value (40.21) and then multiply by 100:
10.05 / 40.21 * 100 = 25
Now that we know we need 25% Kaolin to fulfill the remaining Al2O3, we can calculate the other oxides contributed by Kaolin:
SiO2: 47.29 * .25 = 11.82
The resulting calculation table looks like this:
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
3. Add Dolomite to fulfill MgO and partially CaO
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||
| Dolomite | 3.2 | 0.70 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 12.42 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
4. Add Bone Ash to fulfill P2O5 and some CaO
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||
| Dolomite | 3.2 | 0.70 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 12.42 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Bone Ash | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
5. Add Silica to fulfill remaining SiO2
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||
| Dolomite | 3.2 | 0.70 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 12.42 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Bone Ash | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Silica | 37.52 | 37.52 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 |
6. Add Whiting to fulfill remaining CaO
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||
| Dolomite | 3.2 | 0.70 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 12.42 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Bone Ash | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Silica | 37.52 | 37.52 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||||||
| Whiting | 21.21 | 11.9 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 0.70 | 0.08 |
7. Add Red Iron Oxide to fulfill Fe2O3
| Amount | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O | KNaO | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Analysis | 65.40 | 14.60 | 0.70 | 13.40 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 4.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 24.8 | 16.06 | 4.54 | 4.20 | 4.20 | ||||||
| Remaining | 49.34 | 10.05 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||
| Kaolin | 25 | 11.82 | 10.05 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 0.70 | 13.4 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||
| Dolomite | 3.2 | 0.70 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 12.42 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Bone Ash | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| Remaining | 37.52 | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Silica | 37.52 | 37.52 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 11.9 | 0.70 | 0.08 | ||||||||
| Whiting | 21.21 | 11.9 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 0.70 | 0.08 | |||||||||
| Red Iron Oxide | 0.74 | 0.70 | |||||||||
| Remaining | 0.08 |
8. Fulfilling Titanium
Titanium is a vital component of many types of glazes. In celadons, titanium modifies the color, shifting green from the blue end of the spectrum towards yellow. Titanium often is present in glazes as a contaminant in the clays. For this glaze, some trace amount of titanium will already come from the 25% kaolin. Therefore we can make the decision to not additionally add titanium to the recipe.
Similarly, the amount of iron we add can be changed, as clays often already contain some amount of iron.
Final Glaze Recipe
24.8 Potash Feldspar
25 Kaolin
3.2 Dolomite
0.94 Bone Ash
37.52 Silica
21.21 Whiting
0.74 Red Iron Oxide
Final 100% Glaze Recipe with Red Iron Oxide as an additive
| Material | Amount | Additional |
|---|---|---|
| Silica | 33.3 | |
| Kaolin | 22.2 | |
| Potash Feldspar | 22.01 | |
| Whiting | 18.82 | |
| Dolomite | 2.84 | |
| Bone Ash | 0.83 | |
| Total Base | 100 | |
| Red Iron Oxide | 0.66 | Yes |
| Total | 100.66 |
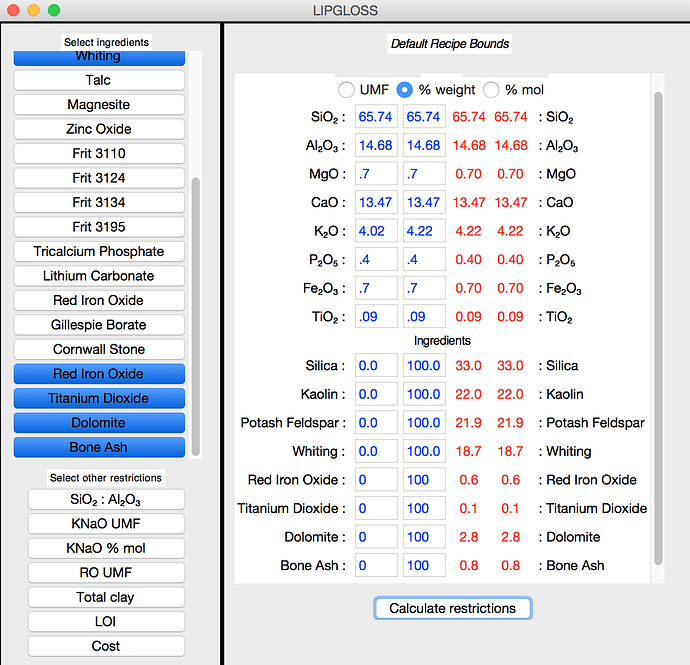
Using Lipgloss
New to Lipgloss? Start here:
https://wiki.glazy.org/t/using-lipgloss/
Lipgloss makes constructing a recipe from an analysis easy. Just select the materials, enter the analysis, and click “Calculate Restrictions”.